Metal Injection Molding vs Die Casting
Metal Injection Molding and Die Casting are two different manufacturing processes for producing metal parts. Here are the key differences between the two processes:
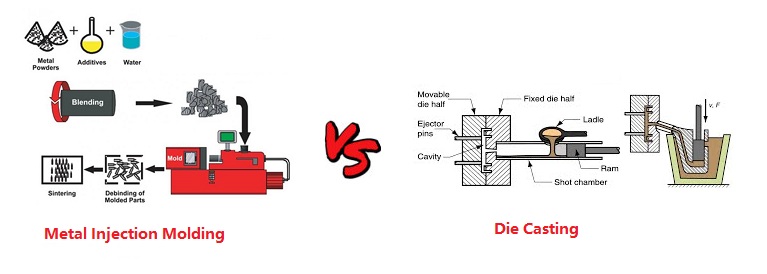
Process: Metal Injection Molding involves mixing metal powder with a binder material to create a feedstock, which is then injected into a mold cavity. The part is heated and the binder is removed, leaving behind a solid metal part. Die casting involves melting metal and injecting it into a mold under high pressure. The metal solidifies quickly, and the part is ejected from the mold.
Material: Metal Injection Molding is typically used with a variety of metals, including stainless steel, tungsten, and titanium. Die casting is typically used with non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, zinc, and copper.
Part size: Metal Injection Molding is well-suited for producing small, intricate parts, while die casting is better for producing larger, more complex parts.
Tolerance: Metal Injection Molding can achieve tighter tolerances than die casting, making it ideal for applications that require high precision and accuracy.
Surface finish: Metal Injection Molding can produce parts with a smoother surface finish compared to die casting.
Manufacturing Cost: Metal Injection Molding can be more expensive than die casting for low volume production runs, but can be cost-effective for high volume production.
Overall, Metal Injection Molding is better suited for small, intricate parts with high precision and accuracy requirements, while die casting is better suited for larger, more complex parts. The choice between the two processes will ultimately depend on the specific requirements of the part being produced, as well as the production volume and cost considerations.